news
Categories
Years
2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 |
2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 |
Last News
Results 81 - 100 of 207.
Health - Pharmacology - 08.01.2026
System which can spot infections in 20 mins could fight antimicrobial resistance
A new technique which slashes the time taken to diagnose microbial infections from days to minutes could help save lives and open up a new front in the battle against antibiotic resistance, researchers say. Engineers and clinicians from the UK and China are behind the breakthrough system, called Autoenricher.
Earth Sciences - 07.01.2026
Human-made materials could make up as much as half of some Scottish beaches
The natural sands of beaches along the Firth of Forth are being mixed with significant amounts of human-made materials like bricks, concrete, glass and industrial waste, new research has revealed. A detailed survey of six beaches led by a team from the University of Glasgow has found that these mineral-based materials, known as anthropogenic geomaterials, now make up far more of the beach surface than previously realised.
Life Sciences - Health - 07.01.2026
First ancient human herpesvirus genomes document their deep history with humans
Analysis of ancient DNA has confirmed that certain human herpesviruses became part of the human genome thousands of years ago, in a study involving a UCL researcher. For the first time, scientists have reconstructed ancient genomes of Human betaherpesvirus 6A and 6B (HHV-6A/B) from archaeological human remains more than two millennia old.
Health - 06.01.2026
University of Manchester researchers have shown that analysis of fluid flushed through a fallopian tube holds promise for providing insights into molecular changes linked to early ovarian cancer development. The analysis - featured in the journal Clinical and translational medicine - revealed molecular signals that in one case prompted re-examination of archived fallopian tube tissue and led to the retrospective identification of a pre-invasive or very early cancerous lesion.
Pharmacology - Health - 06.01.2026
Stopping weight-loss drugs is linked to faster regain than ending diet programmes
New study finds that stopping weight-loss drugs is linked to faster regain than ending diet programmes People tend to regain weight rapidly after stopping weight-loss drugs - and faster than after ending behavioural weight loss programmes - according to a new systematic review and meta-analysis from researchers in Oxford's Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences , published in The BMJ today.
Life Sciences - Health - 05.01.2026
From pint to plate: scientists brew up a new way to grow meat
Yeast left over from brewing beer can be transformed into edible 'scaffolds' for cultivated meat - sometimes known as lab-grown meat - which could offer a more sustainable, cost-effective alternative to current methods, according to a new study from UCL researchers. 'Nose to tail' eating, which emphasises the use of the whole animal, has long been an ethos of sustainability-conscious chefs and diners.
Health - Pharmacology - 23.12.2025
Menopause hormone therapy does not appear to impact dementia risk
A major review of prior research has found no evidence that menopause hormone therapy either increases or decreases dementia risk in post-menopausal women, in a new study led by UCL researchers. The findings, commissioned by the World Health Organisation (WHO) and published in The Lancet Healthy Longevity , add much-needed clarity to a hotly-debated topic, and reinforce current clinical guidance that menopause hormone therapy, also called hormone replacement therapy or HRT, should be guided by perceived benefits and risks and not for dementia prevention.
Environment - Earth Sciences - 23.12.2025

The urgency of the climate crisis demands rapid innovation. Manchester researchers are using AI to assess climate remediation techniques, generating evidence faster to accelerate the development of promising technologies. Can we find ways to lock away carbon at the scale needed to fight climate change? There are lots of promising ideas which can make significant impacts at scale, such as ocean fertilisation, ocean alkalinity enhancement, enhanced rock weathering with croplands - but field trials at scale are slow, expensive and come with potential environmental risks.
Materials Science - Electroengineering - 19.12.2025
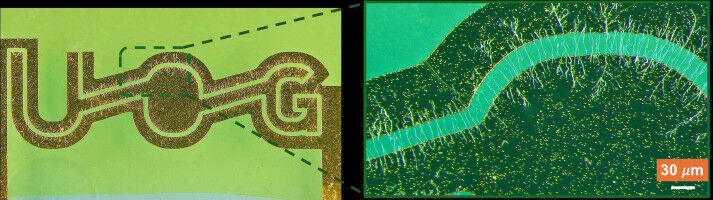
A breakthrough development in nanofabrication could help support the development of new wireless, flexible, high-performance transparent electronic devices. Researchers from the University of Glasgow's James Watt School of Engineering have developed a new method of interfacial imprinting ultra-thin nanowires onto bendable, transparent polymeric substrates.
History & Archeology - Health - 19.12.2025

Research examining ancient sewer drain sediment suggests the Roman soldiers garrisoned at the fort of Vindolanda suffered with intestinal worms and diarrhoea - despite their toilets, baths and drinking water system. These chronic infections likely weakened soldiers, reducing fitness for duty. Helminths alone can cause nausea, cramping and diarrhoea.
Psychology - Innovation - 18.12.2025
’Personality test’ shows how AI chatbots mimic human traits - and how they can be manipulated
Researchers have developed the first scientifically validated 'personality test' framework for popular AI chatbots, and have shown that chatbots not only mimic human personality traits, but their 'personality' can be reliably tested and precisely shaped - raising implications for AI safety and ethics.
Health - Pharmacology - 17.12.2025
Nicotine pouch rise driven by young men
Use of nicotine pouches has risen substantially in Great Britain over the last five years, particularly among young men, with one in 13 (7.5%) men aged 16 to 24 now using them, according to a new study led by researchers at UCL. The study, published in the journal Lancet Public Health and funded by Cancer Research UK, found that use of pouches overall had increased from 0.1 to 1% of all'adults, equivalent to about 522,000 people.
Psychology - Health - 16.12.2025
Specific depressive symptoms in midlife linked to increased dementia risk
Six particular depressive symptoms when experienced in midlife predict dementia risk more than two decades later, finds a new study led by UCL researchers. Midlife depression has long been considered a risk factor for dementia in later life. However, new findings published in The Lancet Psychiatry suggest that this relationship is driven by a small cluster of specific symptoms rather than by depression overall.
Astronomy & Space - 16.12.2025

Astronomers have captured the most detailed images ever taken of a jet launched by a young star, confirming a theoretical model that has remained untested for three decades. Published today in Nature Astronomy , the images reveal a series of delicate, ring-like structures that record decades of violent outbursts during the star's early life.
Life Sciences - Health - 16.12.2025
Scientists Track Adaptation of H5N1 in Dairy Cattle
The H5N1 avian influenza virus - commonly known as bird flu - has been causing outbreaks in dairy cows in the United States since March 2024. Now, scientists studying the adaptation of the avian H5N1 viruses to cows, have found that some of the more recent variants are more able to infect cow cells and tissues than some older variants.
Innovation - 12.12.2025
Tech savvy users have most digital concerns
Digital concerns around privacy, online misinformation, and work-life boundaries are highest among highly educated, Western European millennials, finds a new study from researchers at UCL and the University of British Columbia. The research, published in , also found individuals with higher levels of digital literacy are the most affected by these concerns.
Health - Psychology - 11.12.2025
Body image issues in adolescence linked to depression in adulthood
Teenagers who are unhappy with their bodies are more likely to develop symptoms of eating disorders and depression in early adulthood, according to a new study led by UCL researchers. The research, believed to be the first of its kind, followed more than 2,000 twins born in England and Wales. It found that higher body dissatisfaction at age 16 predicted greater symptoms of eating disorders and depression well into the twenties, even after taking into account family background and genetics.
Innovation - Economics - 11.12.2025
Can AI be a good creative partner?
What generative AI typically does best - recognise patterns and predict the next step in a sequence - can seem fundamentally at odds with the intangibility of human creativity and imagination. However, Cambridge researchers suggest that AI can be a useful creative partner, as long as there is clear guidance on how ideas should be developed together.
Earth Sciences - 11.12.2025
New research highlights golden opportunity for future prospectors
Sophisticated new chemical analysis of gases trapped in rocks for millions of years has cast new light on the origin of the gold deposits beneath Scotland and Ireland. The finding, made by team of scientists led by Professor Fin Stuart from the University of Glasgow, could help pinpoint the location of buried deposits of the treasured metal in the future.
Astronomy & Space - Earth Sciences - 11.12.2025

Strongest evidence yet for an atmosphere on a rocky planet outside our solar system - a thick blanket of gases above an ocean of magma. Researchers using NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have detected the strongest evidence yet for an atmosphere on a rocky planet outside our solar system. Observations of the ultra-hot super-Earth TOI-561 b suggest the exoplanet is surrounded by a thick blanket of gases above a global magma ocean.
Health - Mar 13
Oxford and Serum Institute of India sign IP license agreement to advance NipahB vaccine candidate
Oxford and Serum Institute of India sign IP license agreement to advance NipahB vaccine candidate
Career - Mar 13
Faye Holland joins pioneering Cambridge x Manchester collaboration as Partnership Director
Faye Holland joins pioneering Cambridge x Manchester collaboration as Partnership Director

Economics - Mar 13
£9.6M SATURN-2 programme launched to deliver the UK's next generation of nuclear experts
£9.6M SATURN-2 programme launched to deliver the UK's next generation of nuclear experts

Health - Mar 12
Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences designated as the WHO Collaborating Centre on Primary Health Care
Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences designated as the WHO Collaborating Centre on Primary Health Care

