news
Life Sciences
Results 1 - 20 of 5224.
Life Sciences - Health - 11.03.2026
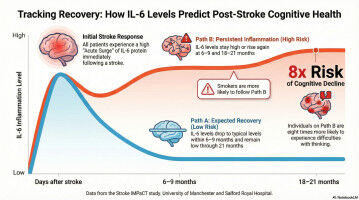
Inflammation-related protein changes could help predict cognitive impairment after a strokeespecially in smokers Researchers at The University of Manchester have found that tracking changes in a protein linked to inflammation (interleukin-6) after a stroke could help identify people at risk of later memory and thinking problems (also known as cognitive problems).
Life Sciences - 10.03.2026
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Scientists have successfully reconstructed videos purely from the brain activity of mice, showing what the mice were seeing, in a new study led by UCL researchers. The findings, published in eLife , could help shed light on the intricate workings of how the brain processes visual information and open new avenues for exploring how different species perceive the world.
Life Sciences - Health - 10.03.2026
Development and sex shape the brain
Two companion studies, published in Cell Genomics , reveal how brain development lays the foundation for both shared and sex-specific circuits, redefining how neural diversity arises. A preview article l'inked to the report highlights the broader significance of these findings and places them in context for the field.
Health - Life Sciences - 09.03.2026
New ’molecular switch’ controlling antiviral immunity identified
A previously unknown chain of molecular signals that determines how strongly the body's immune system responds to viral infection has been discovered by scientists at UCL and the University of Cologne. Pattern recognition receptors act as sensors in the body's immune system that detect the molecular signatures of invading viruses and bacteria.
Life Sciences - Health - 09.03.2026
Worrying extent of imprecise gene and gene mutation naming
A systematic review of 52 scientific papers submitted to a world-leading clinical genetics journal from multiple scientists over a two-year period reveals that not a single one named critical gene mutations (correctly termed as variants) with precision. The findings partly explain why around 70% of rare diseases go undiagnosed, even in the UK, which arguably has the worlds most advanced genomic medicine service.
Pharmacology - Life Sciences - 09.03.2026

The recreational drugs cannabis, cocaine and amphetamines significantly increase the risk of stroke - including among younger users - Cambridge researchers have concluded after analysing data from more than 100 million people. Our analysis suggests that it is these drugs themselves that increase the risk of stroke, not just other lifestyle factors among users Eric Harshfield Stroke is a major global health challenge - the third leading cause of death and disability combined.
Life Sciences - Health - 06.03.2026
The cellular switch that explains why humans aren’t nocturnal
Differences in cellular pathway activity flip the switch from nocturnality to diurnality and explain a major evolutionary change humans have undergone. Early mammals were nocturnal, sleeping during the day while large predators were active. However, after the extinction of dinosaurs, several different lineages of mammals independently transitioned to become active during the day.
Paleontology - Life Sciences - 05.03.2026

The arrival of substantial numbers of early human ancestors ( Homo erectus) in the Southeast Asian prehistoric landmass of Sundaland, approximately 1.8 million years ago, likely triggered an evolutionary shift in Leucosphyrus mosquitoes, according to a new study. Researchers from The University of Manchester suggest that during the Early Pleistocene, the arrival and presence of these early hominins drove the mosquitoes to adapt to feeding on humans.
Life Sciences - Environment - 05.03.2026
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
When a species lives in two distinct types of habitats, individuals with traits better suited to each habitat will thrive and reproduce, naturally selecting descendants with those traits.
Life Sciences - Health - 04.03.2026

A new study from the Royal Veterinary College (RVC) has revealed a unifying mechanical principle that explains why animals as different as pike, tuna, vultures and swifts have evolved such vastly different shapes for flight and swimming. The findings suggest that the same equations used when designing propellers apply to swimming and flapping flight.
Health - Life Sciences - 25.02.2026

Researchers in Manchester have developed an experimental method that shows potential for accurately detecting the most common and aggressive form of brain cancer in adults, known as glioblastoma, from the blood. This pioneering study, led by scientists at the University of Manchester and involving teams in Denmark, has been published in Neuro-oncology Advances [add link to article].
Life Sciences - 20.02.2026
Study sheds new light on early brain development in Down syndrome
Scientists have found new clues about how the brains of people with Down syndrome develop differently from a very early age, in a study led by researchers at UCL and Queen Mary University of London. Brain cells with an extra copy of a chromosome (trisomy 21) - the genetic cause of Down syndrome - have difficulty forming strong, well-coordinated connections with each other, according to the new Nature Communications study.
Life Sciences - 10.02.2026

Researchers from The Universities of Manchester and Birmingham have identified the exact nerve cells in the brain that drive important behavioural changes in female fruit flies after they mate. The discovery, published in the journal eLife today (insert date), sheds light on how animals integrate sensory information to guide reproduction and has, say the researchers, general implications on understanding the brains' role in reproduction.
Health - Life Sciences - 10.02.2026

Just over one in 10 deaths from a wide range of infectious diseases are associated with obesity worldwide, finds a major new study led by a UCL researcher. People with obesity face a 70% higher risk of hospitalisation or death from an infection than those of a healthy weight, suggest the findings published in The Lancet .
Health - Life Sciences - 09.02.2026
’Hidden’ bugs in our gut appear key to good health, finds global study
An understudied group of bacteria in our gut microbiome appears to play a central role in keeping us healthy, according to researchers at the University of Cambridge. These are a fundamental and underappreciated component of human health. Alexandre Almeida In a huge global study led by University of Cambridge researchers, a single group of bacteria - named CAG-170 - has repeatedly shown up in high numbers in the gut microbiomes of healthy people.
Life Sciences - Health - 29.01.2026
How the brain’s ’memory replay’ goes wrong in Alzheimer’s disease
Memory dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease may be linked to impairment in how the brain replays our recent experiences while we are resting, according to a new study in mice by UCL scientists. The researchers say their findings, published in Current Biology , could help scientists develop drug treatments targeting this impaired brain function, or help design new tests for early diagnosis.
Life Sciences - Health - 29.01.2026

Cambridge researchers have revealed a detailed picture of how the human brain grows from mid-pregnancy through the first weeks after birth and identified that sex differences in brain growth are apparent from mid-pregnancy onwards. This study addresses the age-old question of whether nature plays a role in shaping sex differences in the brain Alex Tsompanidis There has long been debate over exactly how early in human brain development sex differences first emerge, and what causes them.
Health - Life Sciences - 28.01.2026
Targeting the gut’s immune system could tackle early stages of Parkinson’s
New research reveals how Parkinson's spreads from the gut to the brain, with the help of immune cells - offering a new potential therapeutic strategy - in a study in mice led by scientists at the UK Dementia Research Institute at UCL. Scientists have long theorised that Parkinson's may start in the gut.
Life Sciences - Paleontology - 28.01.2026
443-million-year-old fossils reveal early vertebrate eyes
A photograph of a second Jamoytius specimen, again with a zinc X-ray map overlain at top, where the eye structure is visible but less well preserved. In this specimen the body scales were also preserved and when mapped for the elements calcium (bottom left) and phosphorous (bottom right) the scales are shown to have the same chemistry as bone.
Health - Life Sciences - 25.01.2026
Lab-grown mini-stomachs could boost understanding of rare diseases
Researchers at UCL and Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) have developed the first-ever lab-grown mini-stomach that contains the key components of the full-sized human organ. Known as a multi-regional assembloid, the pea-sized mini-stomach is the first to contain the fundic region (the upper portion of the stomach), the body (the central region where food is mixed with acid and enzymes), and the antrum (the lower part of the stomach that breaks down food before entering the small intestine).
Health - Mar 13
Oxford and Serum Institute of India sign IP license agreement to advance NipahB vaccine candidate
Oxford and Serum Institute of India sign IP license agreement to advance NipahB vaccine candidate
Career - Mar 13
Faye Holland joins pioneering Cambridge x Manchester collaboration as Partnership Director
Faye Holland joins pioneering Cambridge x Manchester collaboration as Partnership Director

Economics - Mar 13
£9.6M SATURN-2 programme launched to deliver the UK's next generation of nuclear experts
£9.6M SATURN-2 programme launched to deliver the UK's next generation of nuclear experts

Health - Mar 12
Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences designated as the WHO Collaborating Centre on Primary Health Care
Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences designated as the WHO Collaborating Centre on Primary Health Care

